Leicester’s Roman inhabitants lived in a wide variety of houses, ranging from rows of small, simple rectangular buildings built along street fronts (with domestic rooms located behind shops or workshops) to larger, elaborate townhouses built around colonnaded courtyards.
- Leicester’s Roman market-hall or macellum was 43m long, 33m wide and at least 16m high, roughly the same size as Leicester Cathedral
- Archaeologists have found a collapsed wall from the macellum on Highcross Street which was built in a similar manner to the Jewry Wall
- Goods and food were imported to Leicester from across the Roman Empire, including pottery from France, Spain and Italy, and exotic food such as figs, grapes and olives
A Roman market hall, and a delicatessen
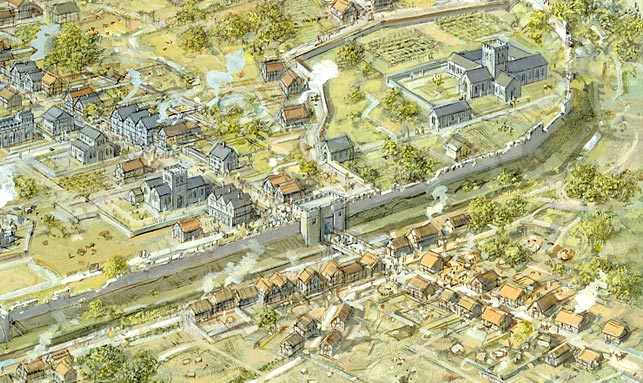
Roman Leicester was a bustling place full of opportunities to work and to shop.
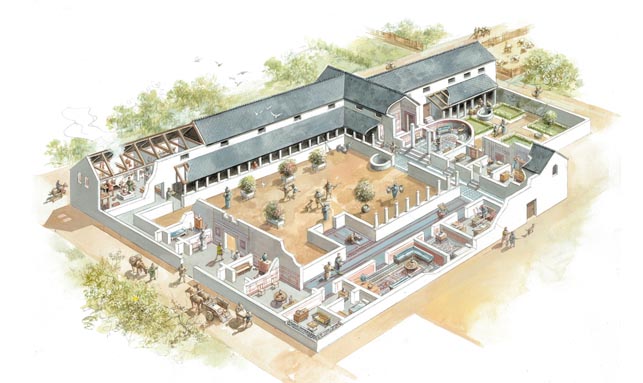
The Roman market-hall
The main shopping centre in Roman Leicester was the forum, but the town’s growing prosperity in the early 3rd century CE necessitated construction of a new market-hall, or macellum, on land to the north. This was built on along similar lines as the forum, with a large aisled hall and ranges of buildings surrounding a courtyard, but it would have been solely devoted to commerce. First discovered in 1958, today it lies opposite the old Free Grammar School on Highcross Street. Its main hall had a simple durable concrete floor but its walls and ceilings were lavishly decorated with painted plaster, and it would have been full of small shops and market stalls – rather like Leicester Market today.
A remarkable archaeological discovery was made in 2006 on the eastern side of Highcross Street. An extensive spread of stone and tile rubble turned out to be the collapsed eastern gable-end wall of the macellum. The area of masonry measured at least 7m by 10m and it was built in a similar manner to the Jewry Wall. Archaeologists were able to calculate that the fallen wall broke off at a level of about 3.6m above the ground and that the macellum would have been at least 16m in height. This is equivalent to a three- or four-storey building today.
The macellum probably fell out of use during the late 4th century after a prolonged period of neglect. Parts of the building may have been destroyed by a large fire. The gable wall finally collapsed during the second half of the 5th century CE.
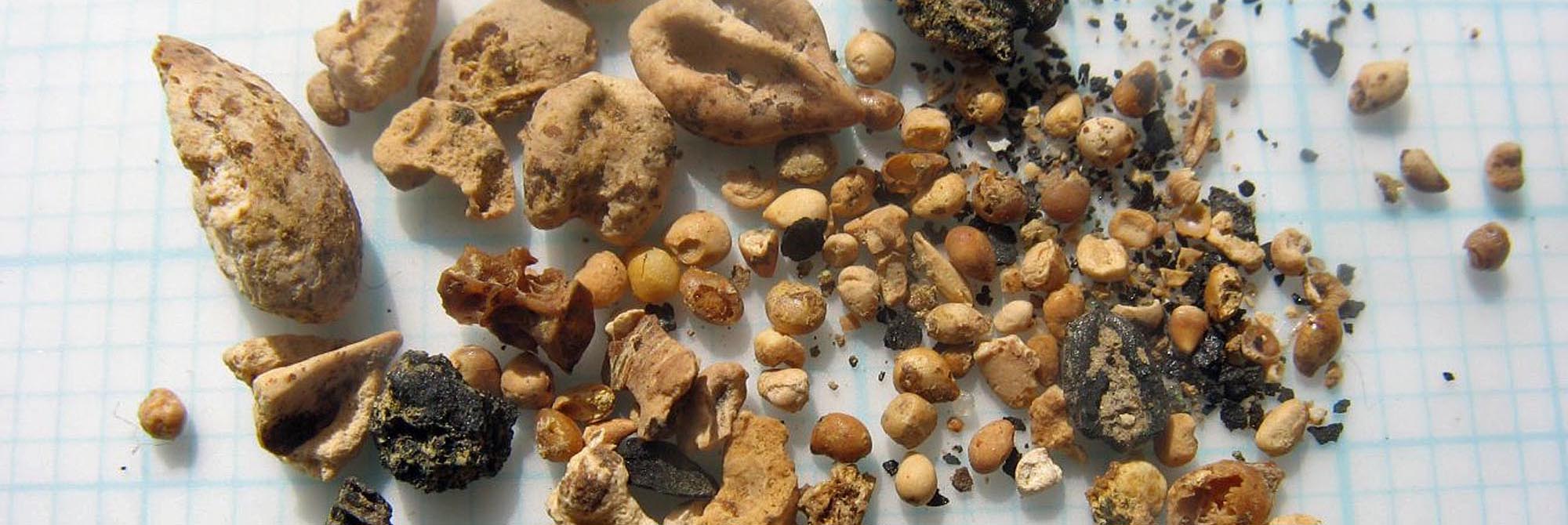

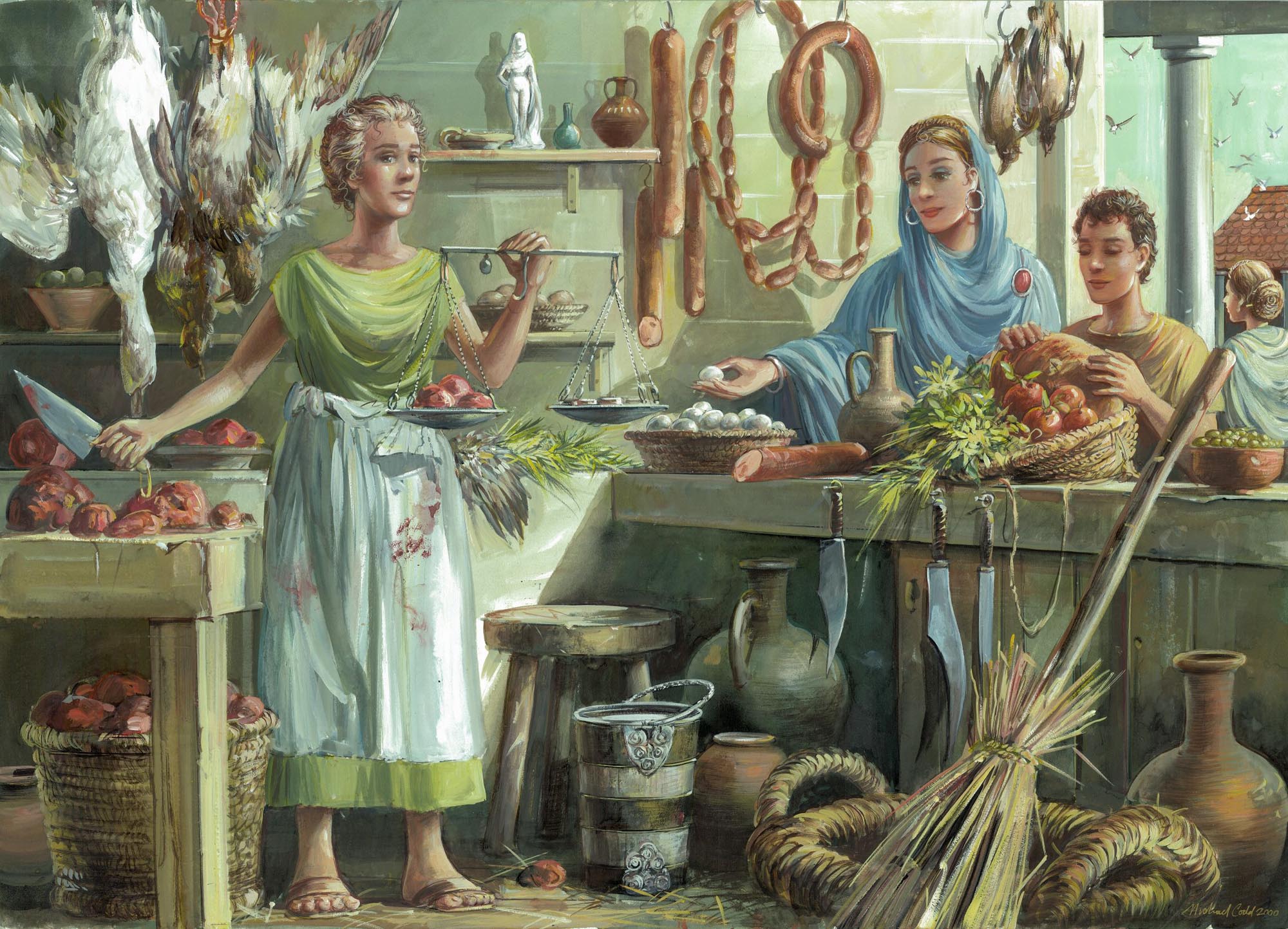
What to eat…
Excavation of part of a Roman building near St Nicholas Circle has identified it as a ‘delicatessen’ selling both local foodstuffs including smoked meat and exotic imports, such as figs, grapes and olives. Broken pottery found in a refuse pit behind the shops was unusual because it was mostly amphorae, bowls, jars and flagons but no drinking vessels, plates or mixing dishes. This suggests food was not being consumed on the premises, like a tavern, but was being stored and displayed for sale.
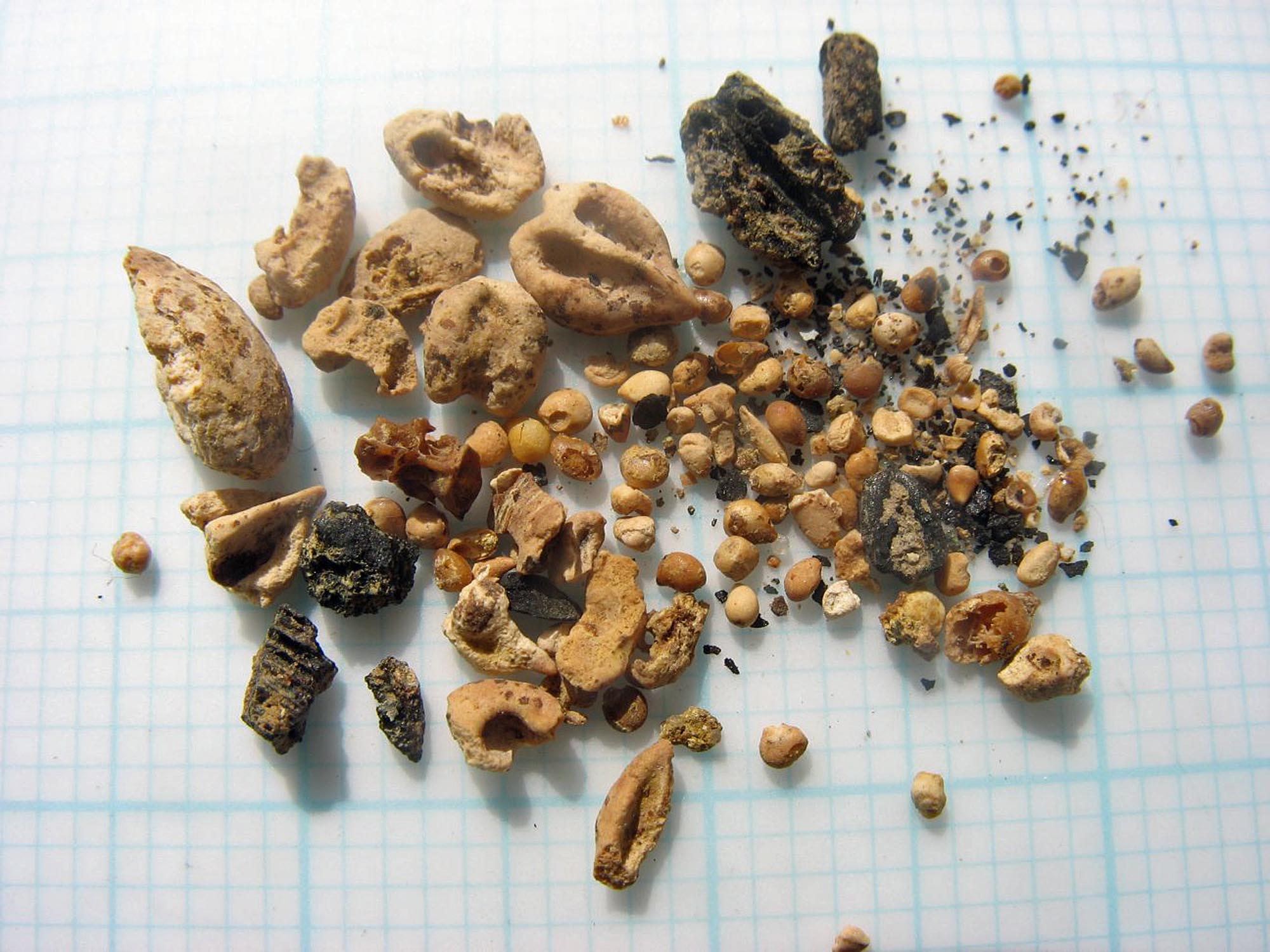
Food remains show that people enjoyed a varied diet. Barley and spelt wheat (used to make bread and porridge, and to thicken stews) were grown locally, along with peas, beans, leaf beets, apples, plums and cherries. Wild foods were also harvested, including hazelnuts, sloes, blackberries, elder and sorrel. People could season dishes with wild mint, coriander, opium poppy and mustard, whilst the wealthy could afford imported foods such as lentils and dried fruits. Meat mostly came from domesticated cattle, sheep, goat, pig and fowl, but wild deer, hare, geese and duck were also hunted. The fish that was consumed comprised mainly eels and herrings, although oysters too were a common food and were probably transported from the Essex coast. Finds of shell indicate that eggs were eaten, but other foods which must have been consumed, such as honey, milk and cheese, have left no trace.
Craft work
Whilst many goods were imported from across the Roman Empire, there is also abundant evidence across Leicester for local craft activities. Iron, bronze, lead, glass, wood, textiles, bone, horn and leather were all being worked and examples of such manufacture include bone pin workshops and a smithy found at Vine Street.
Gallery
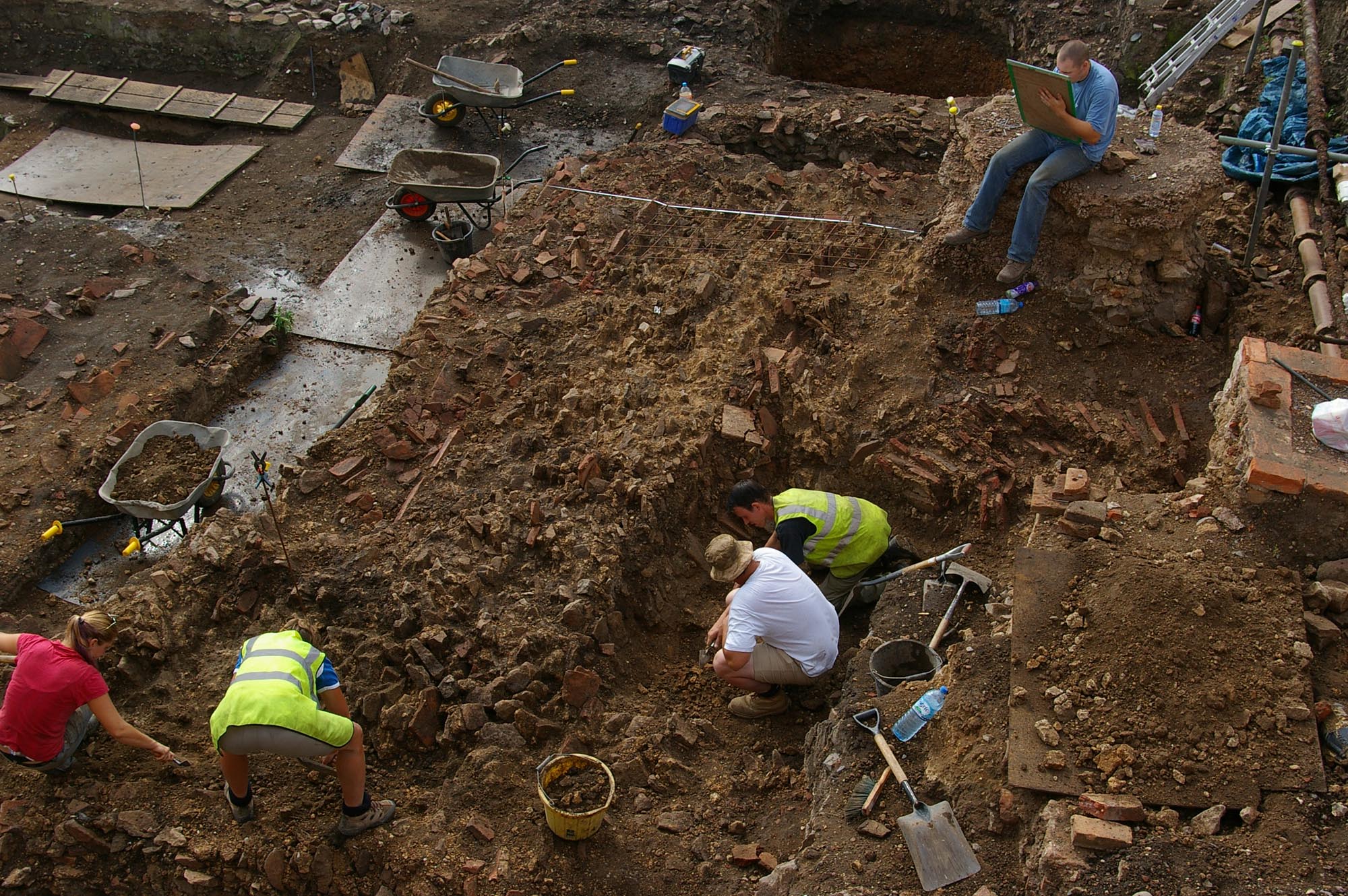

University of Leicester Archaeological Services
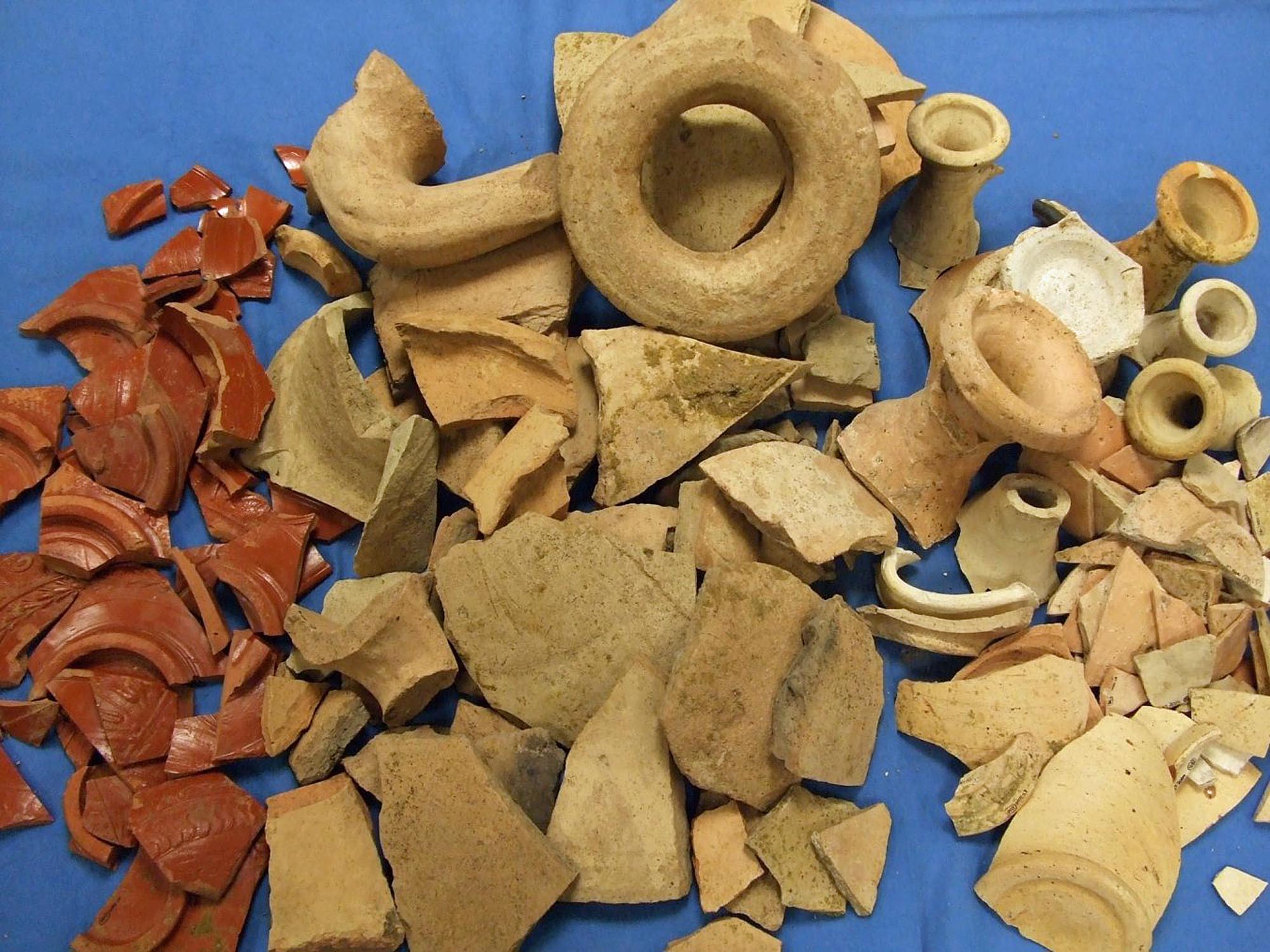

University of Leicester Archaeological Services

Mike Codd / Leicester Arts & Museums Service

University of Leicester Archaeological Services

Leicester Arts & Museums Service

University of Leicester Archaeological Services
The Romans in Leicester
Roman Leicester
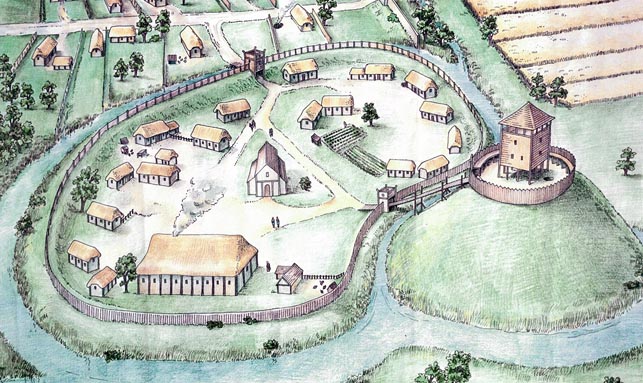
(47- 500) A military fort was erected, attracting traders and a growing civilian community to Leicester (known as Ratae Corieltauvorum to the Romans). The town steadily grew throughout the reign of the Romans.
Medieval Leicester
(500 – 1500) The early years of this period was one of unrest with Saxon, Danes and Norman invaders having their influences over the town. Later, of course, came Richard III and the final battle of the Wars of the Roses was fought on Leicester’s doorstep.
-
The Castle Motte1068

-
Leicester Cathedral1086

-
St Mary de Castro1107

-
Leicester Abbey1138

-
Leicester Castle1150

-
Grey Friars1231

-
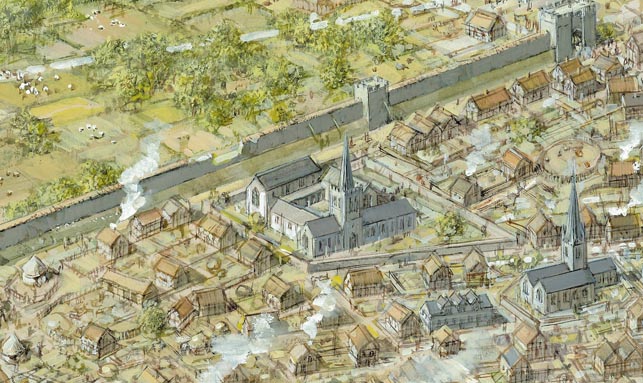
The Streets of Medieval Leicester1265

-
Leicester Market1298

-
Trinity Hospital and Chapel1330

-
Bow Bridgecirca 1350

-
Church of the Annunciation1353

-
John O’Gaunt’s Cellar1361

-
St John's Stone1381

-
Leicester Guildhall1390

-
The Magazine1400

-
The Blue Boar Inn1400

-
The High Cross1577

Tudor & Stuart Leicester
(1500 – 1700) The wool trade flourished in Leicester with one local, a former mayor named William Wigston, making his fortune. During the English Civil War a bloody battle was fought as the forces of King Charles I laid siege to the town.
Georgian Leicester
(1700 – 1837) The knitting industry had really stared to take hold and Leicester was fast becoming the main centre of hosiery manufacture in Britain. This new prosperity was reflected throughout the town with broader, paved streets lined with elegant brick buildings and genteel residences.
-
Great Meeting Unitarian Chapel1708

-
The Globe1720

-
17 Friar Lane1759

-
Black Annis and Dane Hills1764

-
Leicester Royal Infirmary1771

-
New Walk1785

-
Freemasons’ Hall1790

-
Gaols in the City1791

-
Friars Mill1794

-
City Rooms1800

-
Development of Highfields1800

-
Wesleyan Chapel1815

-
20 Glebe Street1820

-
Charles Street Baptist Chapel1830

-
Glenfield Tunnel1832

-
James Cook1832

Victorian Leicester
(1837 – 1901) The industrial revolution had a huge effect on Leicester resulting in the population growing from 40,000 to 212,000 during this period. Many of Leicester's most iconic buildings were erected during this time as wealthy Victorians made their mark on the town.
-
Leicester Union Workhouse1839

-
Campbell Street and London Road Railway Stations1840

-
The Vulcan Works1842

-
Belvoir Street Chapel1845

-
Welford Road Cemetery1849

-
Leicester Museum & Art Gallery1849

-
King Street1850

-
Cook’s Temperance Hall & Hotel1853

-
Amos Sherriff1856

-
Weighbridge Toll Collector’s House1860

-
4 Belmont Villas1862

-
Top Hat Terrace1864

-
Corah and Sons - St Margaret's Works1865

-
Kirby & West Dairy1865

-
The Clock Tower1868

-
Wimbledon Works1870

-
The Leicestershire Banking Company1871

-
St Mark’s Church and School1872

-
Victorian Turkish Baths1872

-
The Town Hall1876

-
Central Fire Stations1876

-
Aylestone Road Gas Works and Gas Museum1879

-
Gas Workers Cottages1879

-
Leicestershire County Cricket Club1879

-
Welford Road Tigers Rugby Club1880

-
Secular Hall1881

-
Development of Highfields1800

-
Abbey Park1881

-
Abbey Park Buildings1881

-
Victoria Park and Lutyens War Memorial1883

-
Leicester Fosse FC 18841884

-
Leicester Coffee and Cocoa Company Coffee Houses1885

-
St Barnabas Church and Vicarage1886

-
Abbey Pumping Station1891

-
Luke Turner & Co. Ltd.1893

-
West Bridge Station1893

-
Thomas Cook Building1894

-
The White House1896

-
Alexandra House1897

-
Leicester Boys Club1897

-
Grand Hotel and General Newsroom1898

-
Highfield Street Synagogue1898

-
Western Park1899

-
Asfordby Street Police Station1899

-
Leicester Central Railway Station1899

Edwardian Leicester
(1901 – 1910) Electric trams came to the streets of Leicester and increased literacy among the citizens led to many becoming politicised. The famous 1905 ‘March of the Unemployed to London’ left from Leicester market when 30,000 people came to witness the historic event.
-
YMCA Building1900

-
The Palace Theatre1901

-
Pares's Bank1901

-
Coronation Buildings1902

-
Halfords1902

-
High Street1904

-
George Biddles and Leicester's Boxing Heritage1904

-
Municipal Library1905

-
Leicester Boys Club1897

-
The Marquis Wellington1907

-
Guild Hall Colton Street1909

-
Women's Social and Political Union Shop1910

-
Turkey Café1901

Early 20th Century Leicester
(1910 – 1973) The diverse industrial base meant Leicester was able to cope with the economic challenges of the 1920s and 1930s. New light engineering businesses, such as typewriter and scientific instrument making, complemented the more traditional industries of hosiery and footwear manufacturing.
-
Dryad Handicrafts1912

-
De Montfort Hall1913

-
Leicester During the First World War1914

-
Fox’s Glacier Mints1918

-
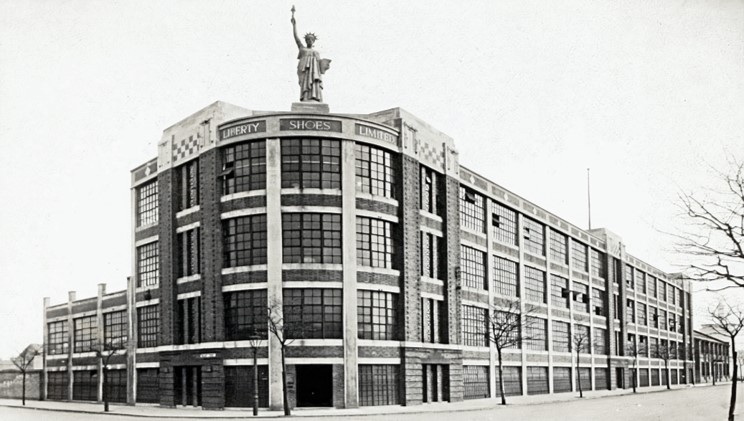
Statue of Liberty1919

-
Housing in Saffron Lane1924

-
Winstanley House1925

-
Housing in North Braunstone1926

-
Lancaster Road Fire Station1927

-
The Little Theatre1930

-
Saffron Hill Cemetery1931

-
Braunstone Hall Junior School1932

-
Former City Police Headquarters1933

-
Savoy Cinema1937

-
Eliane Sophie Plewman1937
-
City Hall1938

-
Athena - The Odeon Cinema1938

-
The Blitz in Highfields1940

-
Freeman, Hardy and Willis - Leicester Blitz1940

-
Leicester Airport1942

-
Leicester’s Windrush Generations1948

-
Netherhall Estate1950
-
Housing at Eyres Monsell1951

-
Silver Street and The Lanes1960

-
Bostik1960

-
Auto-Magic Car Park (Lee Circle)1961

-
University of Leicester Engineering Building1963

-
Sue Townsend Theatre1963

-
Central Mosque1968

-
Belgrave Flyover1973

Modern Leicester
(1973 – present day) Industry was still thriving in the city during the 1970s, with the work opportunities attracting many immigrants from all over the world. While industry has declined in recent years, excellent transport links have made Leicester an attractive centre for many businesses. The City now has much to be proud of including its sporting achievements and the richness of its cultural heritage and diversity.
-
Haymarket Theatre1973

-
The Golden Mile1974

-
Acting Up Against AIDS1976

-
Belgrave Neighbourhood Centre1977

-
Diwali in Leicester1983

-
Leicester Caribbean Carnival1985

-
Samworth Brothers1986

-
Jain Centre1988

-
Guru Nanak Dev Ji Gurdwara1989

-
King Power Stadium2002

-
LCB Depot2004

-
Curve2008

-
BAPS Shri Swaminarayan Mandir2011

-
Makers Yard2012

-
VJ Day 80th Anniversary2020

- Roman Leicester
- Medieval Leicester
- Tudor & Stuart Leicester
- Georgian Leicester
- Victorian Leicester
- Edwardian Leicester
- Early 20th Century Leicester
- Modern Leicester